The future of product development and manufacturing
Fusion integrates all the tools for product creation from the idea to the final product into one comprehensive platform. Whether it is 3D design and modeling, drawing documentation, product visualization and development in simulations and generative designs, or final production.
All functions are designed to give the designer, engineer, technologist or manager as many tools as they need.
To be able to develop and manufacture products even easier - faster - more diverse.
Thanks to the fact that it is a cloud-based product, all work processes can be transferred live between different departments of the company. For example, a designer can design the geometry of a rib, while a simulation engineer is already simulating the heat transfer in the product
or analysing the strength of the structure. Meanwhile, the technologist can prepare the actual production technology, as any changes in the design are automatically reflected in the production.
This gives everyone access to real-time results.

Fusion functions
3D Modelling and Design
A comprehensive set of modelling and analysis tools can be used to design the shape and function of products.
Sketches
Sketches contain a set of geometric entities, the shape and dimension can be defined by annotations and constraints.
Direct modelling
Edit or correct imported geometry from non-native file formats. Design changes can be made without taking into account the model creation history.
Surface modelling
The Surface Modeler allows you to create complex parametric surfaces, patches, templating or geometry correction.
Parametric modelling
With parametric modeling, you can create and modify 3D models by defining parameters such as dimensions, joints and constraints. This feature allows you to make design changes quickly and easily.
Mesh Modelling
Edit and repair imported scans or network models, including STL and OBJ files.
Freeform modelling
Creating complex sub-surfaces using T-spline surfaces and subsequent editing is intuitive using push-pull gestures.
Sheets
Design of sheet metal parts using 2D drawings and DXF. Sheet metal parts can be bent, profiled and unfolded to create waterjet, laser or plasma paths.
Assemblies
Definition of relationships and connections between components, definition and analysis of assembly movement.
Visualization
Render photorealistic images of the model with local or cloud storage. You can set background, lighting, texture mapping and other important features.
Animation
Moving parts in an animation that can be used, for example, to demonstrate product functionality to customers.
Generative design
Explore product design options in many variations that meet design specifications while reducing weight, improving performance and consolidating parts through generative design.
Simulation
Testing designs to make sure they stand up to real-world conditions. With digital product simulation, costs can be reduced by not having to prototype products through real production.
Thanks to cloud-based simulations, there is no need for expensive hardware.
Production
CNC machine programming using intuitive operations for 2-axis to 5-axis machining.
Full associativity between design and machining operations ensures that any changes to the model are reflected in the machining. Machining geometry and parameters can be defined by directly selecting entities from the model.
Features such as efficient adaptive roughing operations, simple tool indexing and accurate machining simulation are available.
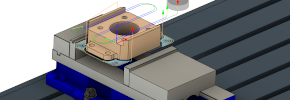
2 axis milling
2 axis toolpaths for controlling CNC routers, milling machines, wire cutters, waterjets, lasers and other equipment. Direct geometry selection from the model and tool correction activation.

3 axis milling
A range of powerful 3-axis machining strategies ensure the rapid creation of high-quality NC codes for roughing and finishing 3D parts. Intuitive workflows simplify the programming of individual features or entire parts.

Multi-axis indexed milling
Multi-axis machining using 3+1 and 3+2 (indexed) machining allows parts to be machined with fewer fixtures and using shorter tool setups. This increases the accuracy of the parts produced and reduces machining cycle times.
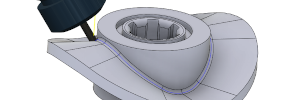
Multi-axis continuous milling
Dedicated 4- and 5-axis toolpaths. Multi-axis tool control and automatic collision avoidance help achieve safe, smooth and predictable machine movement and excellent surface quality.

Turning and powered tools
The combination of milling and turning operations produces NC code that enables the creation of more complex parts made on turning-milling centers.

Probing and inspection
The measuring probes can be used to locate the workpiece prior to machining to determine the exact start of machining. It is also possible to check the dimensions of individual elements on the model.

Hole Recognition
It automates the hole making process by being able to locate all holes on the model. It sorts them by diameter, hole orientation and offers a possible process from drilling, boring, tapping or even countersinking.

Machine simulation
Machine simulation allows you to simulate toolpaths on the machine's digital twin. Using this feature is a simple, easy and accurate way to check if your toolpaths are safe to run on the machine tool.
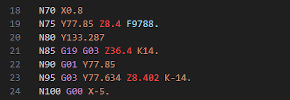
Postprocessors
Fusion comes with numerous postprocessor configurations. Each postprocessor can be customized to meet specific user requirements. Our goal is to produce NC code that is 100% ready to use for your machine tool.








